[ad_1]

Security research from Mandiant and Google indicates that targeting by APT43 and its subset Archipelago aligns with North Korean interests.
Jump to:
Who is APT43?
New research from Mandiant exposes APT43, a cyberespionage threat actor supporting the interests of the North Korean regime; the group is also referred to as Kimsuky or Thallium. ATP43 focuses on collecting strategic intelligence by running credential harvesting attacks and by using social engineering to successfully compromise its targets.
According to Mandiant, who has tracked APT43 since 2018, the threat actor aligns with the mission of the Reconnaissance General Bureau, the main foreign intelligence service from North Korea.
In terms of attribution indicators, APT43 has shared infrastructure and tools with known North Korean operators and North Korean threat actors. In particular, malware and tools have been shared between APT43 and the infamous Lazarus threat actor.
What is the Archipelago threat actor?
In a recent report, Google’s Threat Analysis Group provides intelligence about a threat actor dubbed Archipelago, which they describe as a subset of APT43 activities they’ve been tracking since 2012.
Who does APT43 target?
The APT43 group primarily targeted foreign policy and nuclear security issues, yet it switched in 2021 to targeting health-related verticals, probably due to the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic.
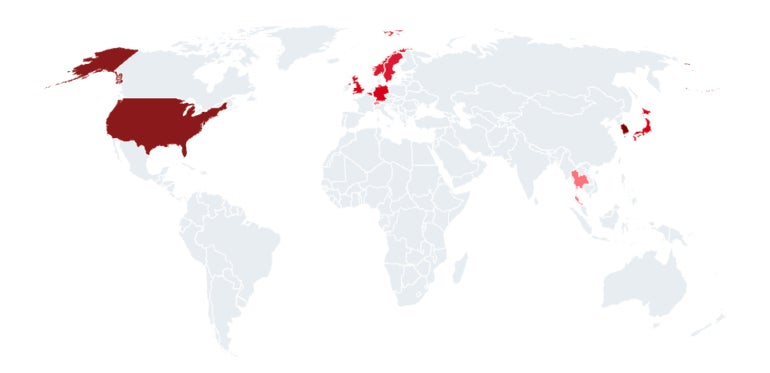
APT43 targets South Korea and the U.S., as well as Japan and Europe, especially in manufacturing against goods whose export to North Korea has been restricted such as fuel, machinery, metals, transportation vehicles and weapons. In addition, the group targets business services, education, research and think tanks with a focus on geopolitical and nuclear policy, and governmental entities (Figure A).
Figure A
APT43 also carries out cybercrime operations likely to fund itself and the regime.
Who does Archipelago target?
The Archipelago subset of APT43 has been observed targeting government and military personnel, think tanks, policymakers, academics and researchers in South Korea, the U.S. and elsewhere.
APT43’s spear phishing and social engineering techniques
APT43 mostly uses spear phishing as a way to compromise its targets. The group often creates convincing personas or spoof key individuals’ identities. Once they compromise such a key person, they might use the person’s contact list for additional spear phishing targeting.
The threat actor sometimes poses as reporters or think-tank analysts to bring targets to provide them with their expert knowledge by asking them specific questions (Figure B).
Figure B

A technique exposed by Google reveals that Archipelago often sends phishing emails in which they masquerade as a representative of a media outlet or think tank asking the target for an interview. A click on a link is needed to see the questions, yet it redirects the victim to a fake Google Drive or Microsoft 365 login page. After the victim enters their credentials, the person is redirected to a document with questions.
Google reports that Archipelago often interacts with a victim for several days or weeks and establishes trust before sending a malicious link or malicious file.
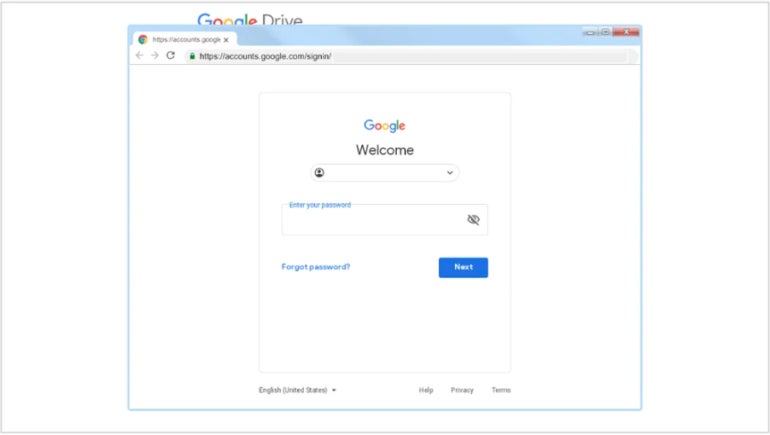
Archipelago might use browser-in-the-browser techniques to trick users who see a fake browser window inside the actual browser window. The fake window shows a legitimate domain to entice users to provide their credentials to the attackers (Figure C).
Figure C
Another technique used by Archipelago consists of sending benign PDF files supposedly from some entity who informs the target about malicious logins they should check (Figure D).
Figure D

APT43’s use of malware families and tools
APT43 relies on several malware families and tools. Public malware families used by APT43 include Gh0st RAT, Quasar RAT and Amadey, yet the threat actor mostly uses a nonpublic malware known as LATEOP or BabyShark, probably developed by the group.
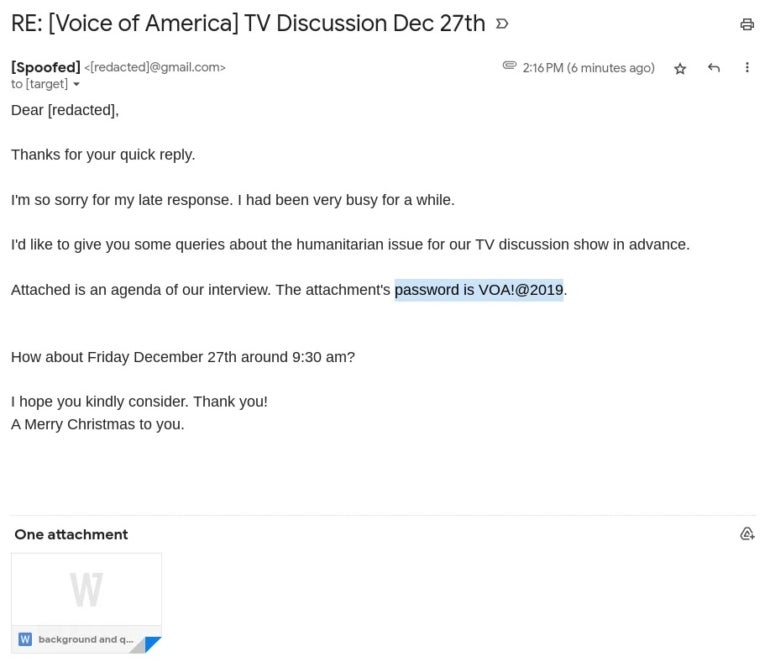
Archipelago has recently incorporated more malware in their operations, often using password-protected attachments as a way to bypass antivirus scanning (Figure E).
Figure E
Archipelago made experiments using a then new technique based on files hosted on Google Drive. Small malicious payloads were encoded directly in filenames of 0 bytes content files. Filenames for files hosted on Google Drive also contained C2 server names, yet Google disrupted that activity, and the group stopped using such techniques on Google Drive.
ISO files were used by Archipelago to deliver malware contained in a zip file. Once the password-protected zip file was unzipped, a document installed VBS-based malware related to BabyShark known to be used by APT43.
More recently, Archipelago tried to use a malicious Chrome browser extension named SHARPEXT, which is able to parse and exfiltrate emails from active Gmail or AOL mail tabs. As a result, Google improved security in the Chrome extension ecosystem, making it much harder for attackers to deploy that malicious extension.
APT43’s interest in cryptocurrency
According to Mandiant, APT43 has a particular interest in cryptocurrencies, which they use for purchasing infrastructure and hardware devices to sustain its operations.
To cover their tracks, APT43 makes use of hash rental services and cloud mining services, which can be used to mine cryptocurrency without any blockchain association to the buyer’s original payments.
In addition, APT43 used a malicious Android application to target Chinese users interested in cryptocurrency loans and harvest for credentials.
How to protect from this APT43 security threat
- Educate users about the social engineering techniques used by APT43 and Archipelago.
- Train users to detect phishing attempts and immediately report it to their security staff.
- Use security solutions to detect phishing emails or malware infection attempts.
- Keep operating systems and software up to date and patched.
Experts in geopolitics and international policies in particular should be trained to detect an approach from an attacker masquerading as a journalist or reporter. Careful triage and examination of such people approaching experts must be done prior to any exchange of information or intelligence.
Disclosure: I work for Trend Micro, but the views expressed in this article are mine.
[ad_2]
Source link



