[ad_1]
GitHub wants you to protect your account with the right type of authentication.

GitHub is now prompting developers and administrators who use the site to secure their accounts with two-factor authentication. The move toward two-factor authentication for all such users officially started on March 13 and will be a requirement by the end of 2023, GitHub said in a recent blog post.
GitHub will gradually roll out the process to different groups throughout the year and scale up as 2023 progresses. If you receive an alert from GitHub, you’ll have 45 days to enable 2FA on your account. But why wait until then?
How to secure your GitHub account with 2FA
To secure your GitHub account now, you can choose from a few 2FA methods, including SMS, a security key, the GitHub mobile app or an authenticator app; however, GitHub recommends a security key, the mobile app or an authenticator app as the strongest options. Whichever method you choose, there are specific steps to follow to set up your GitHub account with 2FA.
Sign into the GitHub site
1. Browse to the GitHub site and sign in with your individual account.
2. Click your account icon in the upper right and select Settings.
3. At the Settings screen, click the option on the left for Password And Authentication.
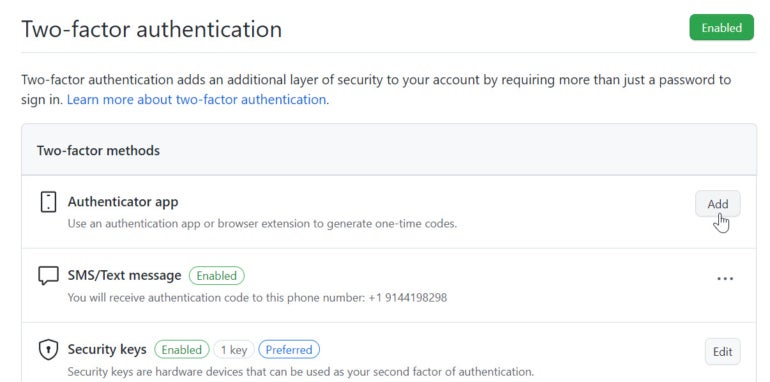
4. Click the button for Enable Two-Factor Authentication (Figure A).
Figure A
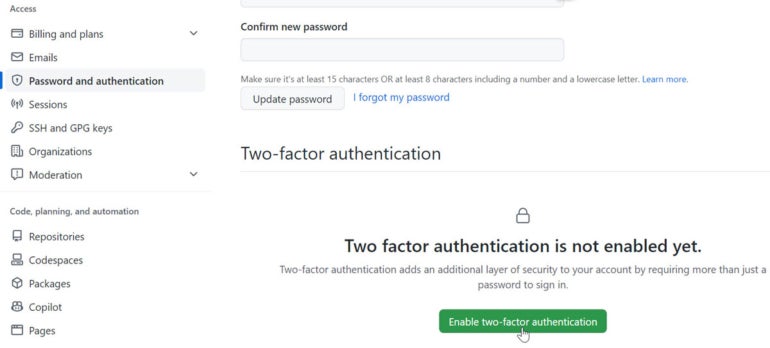
Choose the first authentication method
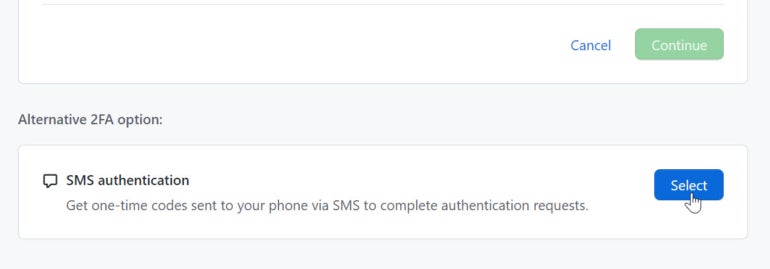
The next screen offers you two options: Authenticator App and SMS Authentication. Rather than choosing only one option, you can pick them both; this way, if one method isn’t available, you can turn to the other. The SMS authentication is a good place so start, so click the Select button for that option (Figure B).
Figure B
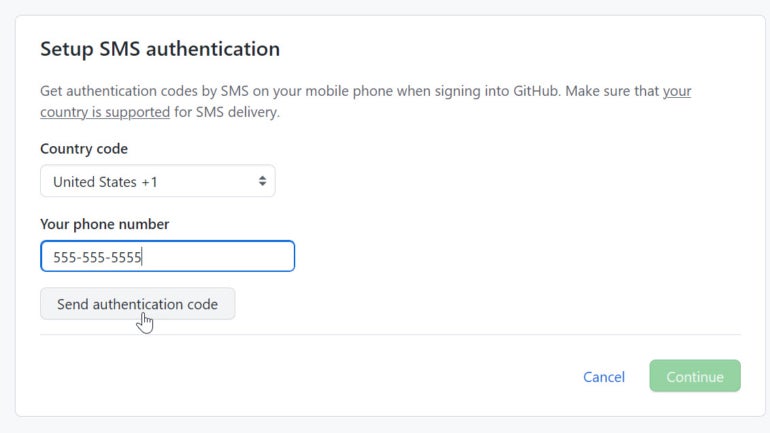
At the next screen, enter your full phone number and click the button for Send Authentication Code (Figure C).
Figure C
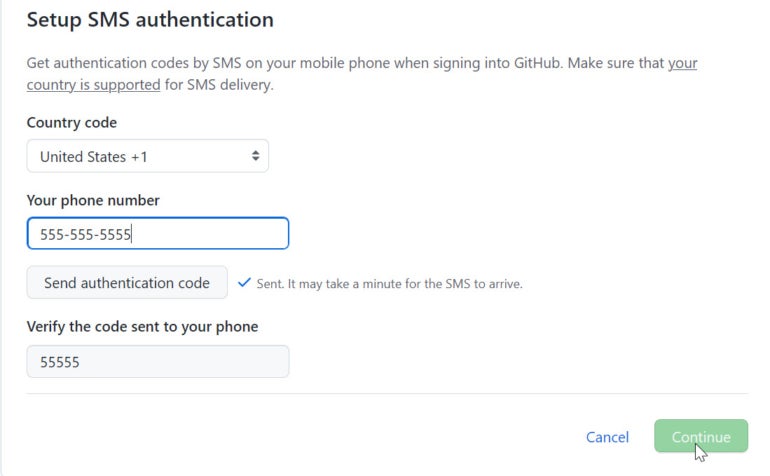
Enter the authentication code in the appropriate field (Figure D).
Figure D
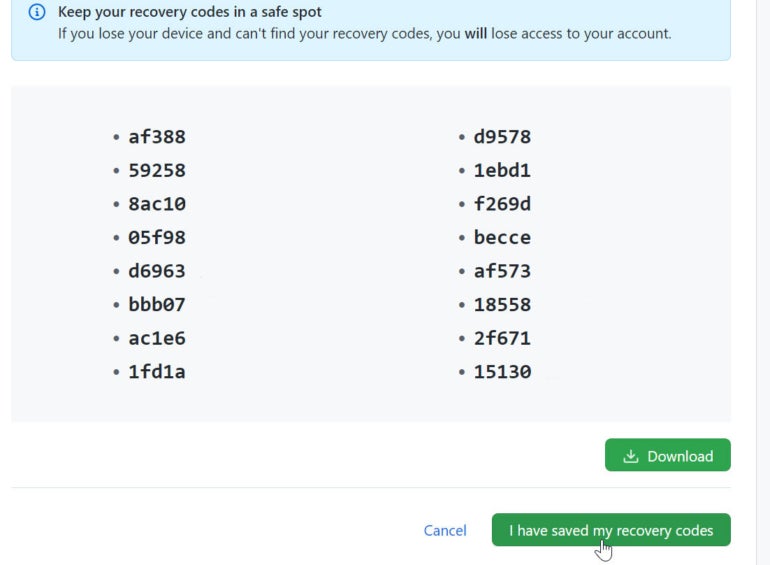
The next screen displays a list of recovery codes that you can use if you ever lose your phone. Download the recovery codes as a plain text file to your PC and save the file in a safe place. Then, click the button indicating that you have saved your recovery codes (Figure E).
Figure E
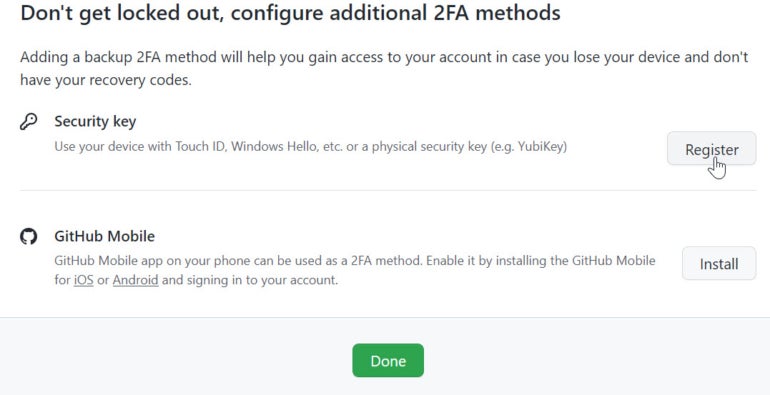
Choose additional verification methods
After establishing the SMS verification, GitHub urges you to set up additional methods, especially since SMS messaging is the least secure one. The option for security key lets you use either a physical security key or a biometric method such as Windows Hello. Click the Register button next to Security Key and then type a nickname for this key (Figure F).
Figure F
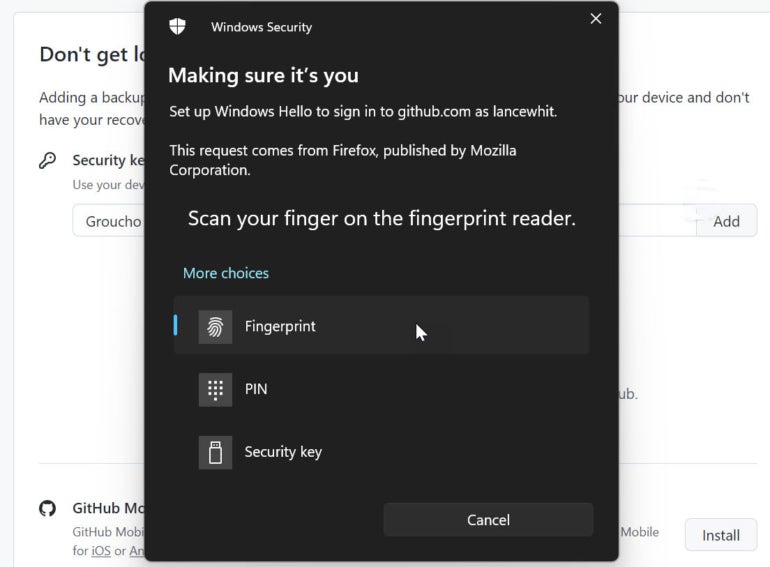
A window pops up asking how you want to authenticate your GitHub account: Face, Fingerprint, PIN or Security Key. Choose the option you prefer, and follow the steps to implement it (Figure G).
Figure G
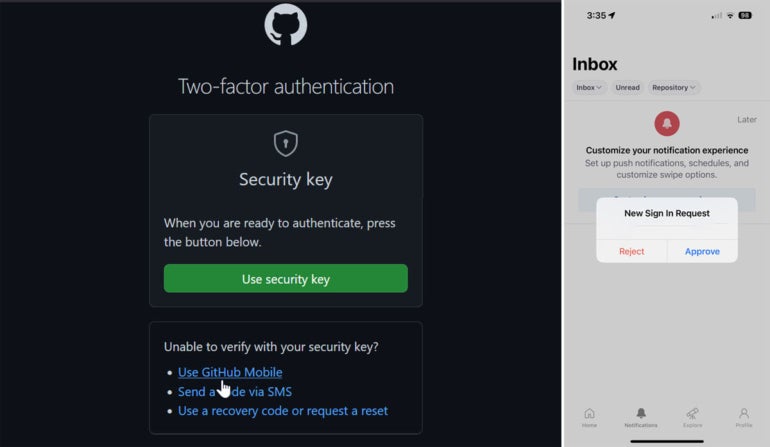
Another option is to use the GitHub mobile app. Click the Install button next to GitHub Mobile to see links to download the app for iOS and Android. Download and install the GitHub app on your phone. Open the app and sign into it.
The next time you log into GitHub on your PC, you’ll see the different 2FA methods available. To use the app, click the link for GitHub Mobile. Open the GitHub app on your phone and approve the request — now you’ll then be signed in on your PC (Figure H).
Figure H
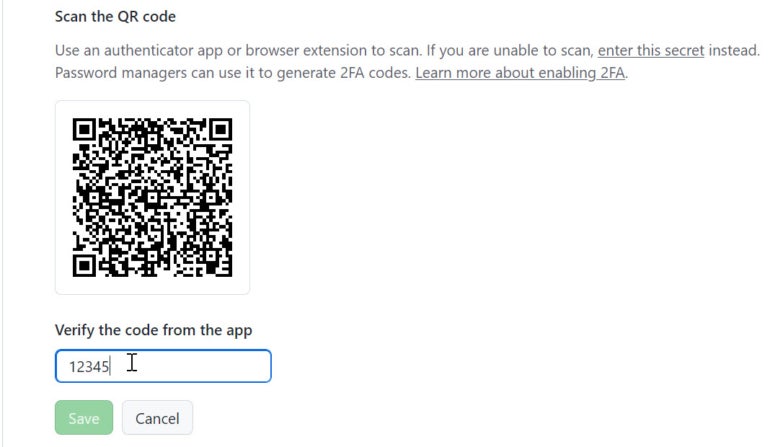
You can set up 2FA for GitHub through an authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, 1Password or Authy. Return to the two-factor authentication screen under Password And Authentication and click the Add button next to Authenticator App (Figure I).
Figure I
Open the authenticator app on your phone and select the option for scanning a QR code. Enter the code displayed in the app in the appropriate field at the GitHub site. Then click Save (Figure J).
Figure J
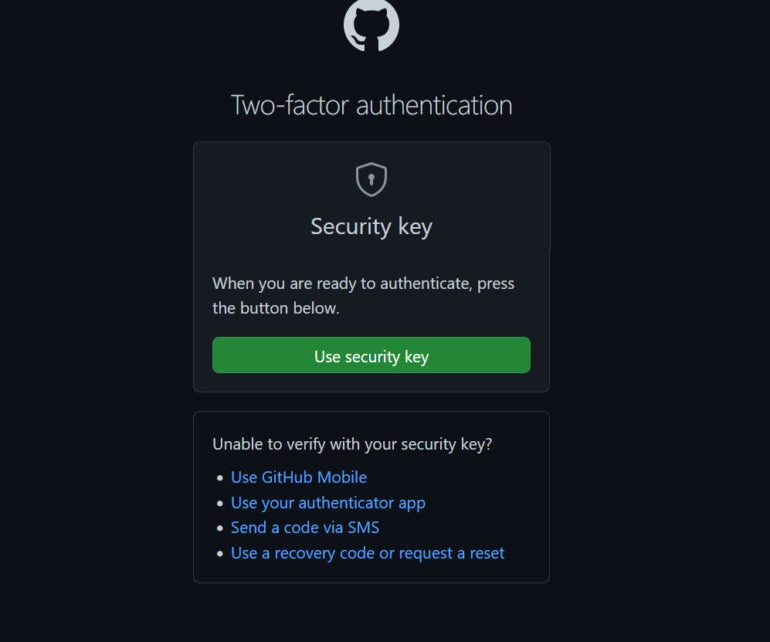
Sign into GitHub
Now whenever you sign into GitHub on a computer or mobile device, you can use any of the 2FA methods that you set up. But keep in mind that a security key, the GitHub mobile app or an authenticator app are the most secure methods for protecting your account (Figure K).
Figure K
[ad_2]
Source link



